3D Printing in Construction: Uses & Application
3D printing has created quite a buzz in the last few years, making people awe-filled with its potential impact on the manufacturing industry. But when it comes to using 3D printing technology in the construction industry, the result is unbelievable. This blog introduces you to the use of 3D printing in the construction industry. First, the concept:
What is 3D Printing?
The process of creating a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model is known as 3D printing. It can be accomplished through several processes in which material is deposited, joined, or solidified under computer control, typically with layers of the material mixed.
One of the primary benefits of 3D printing is the ability to produce extremely complex shapes or geometries that would be impossible to construct by hand. 3D printing can create any type of model or prototype, as well as a damaged component of a product. The most common 3D printing process currently in use is fused deposition modeling (FDM), which employs a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material.
How Impactful are 3D Printing Applications in Construction?
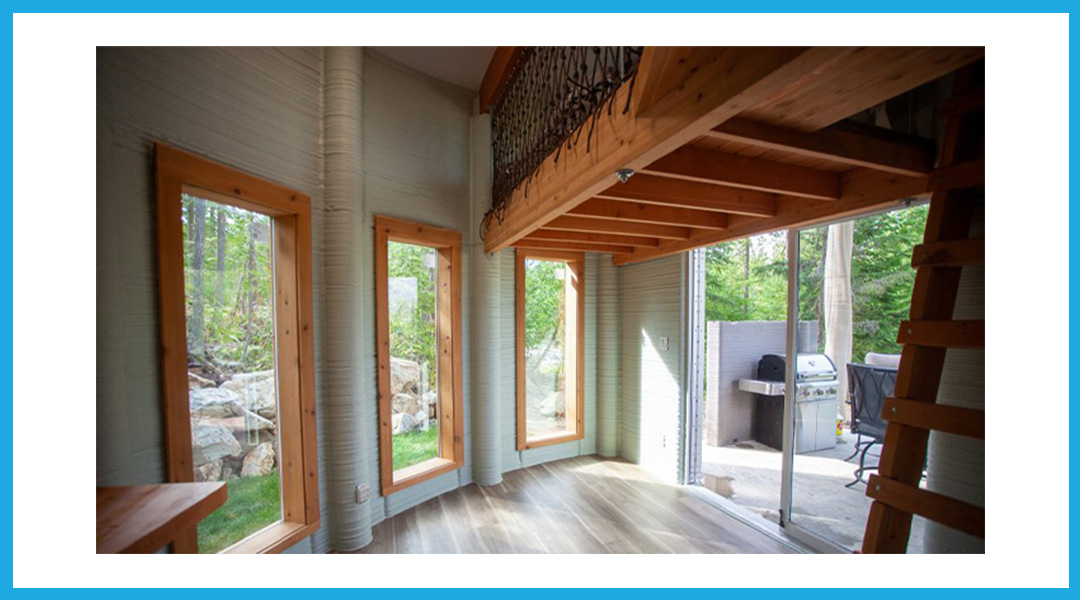
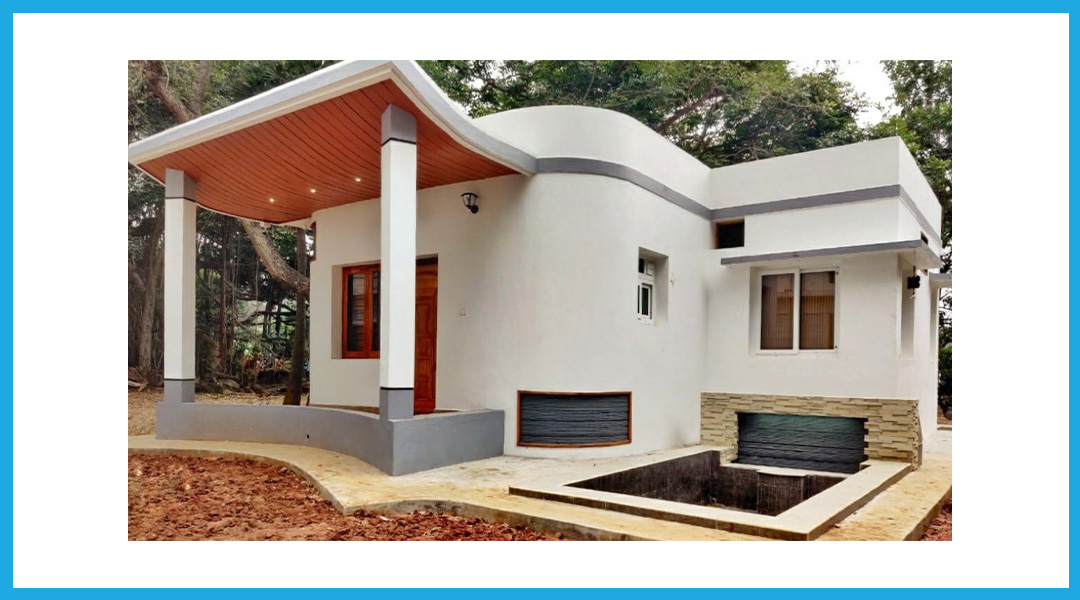
The construction industry is one of the most exciting applications of 3D printing technology. 3D printing is now being used to build entire houses, offices, and other structures that can be of multiple stories or span thousands of square feet.
3D-printed structures can be built using a fraction of the time, labor, and material compared to traditional structures. Small 3D-printed houses are being constructed in less than 24 hours.
The 3D printed structures may not only provide a solution to the affordable housing crisis but also a way for low-cost and time-bound urbanization programmes. The immense potential of 3D-printed buildings is one of the most significant construction and design trends for civil engineers today.
How are 3D Printed Homes Constructed?
While the idea of a giant printer printing a real-life house may seem like much of a fantasy, 3D printing technology has made it a reality. Below are the steps it takes to build a 3D-printed home, from the blueprint to the finishing touches.
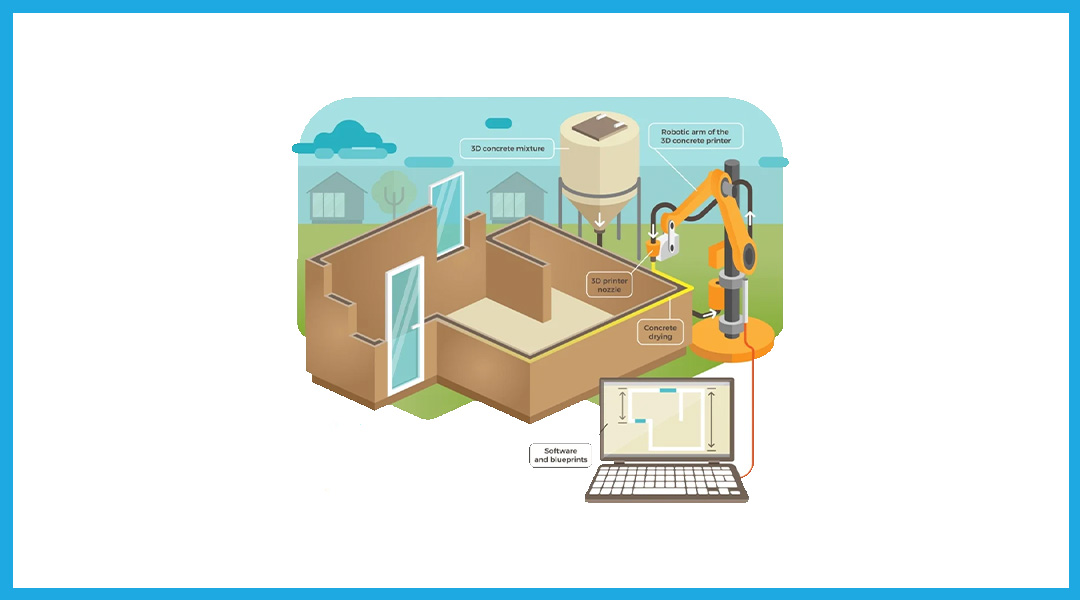
The 3D printer for construction with rails has to be installed/erected around the building site before printing begins.
1. Make a design blueprint.
The first step in the 3D-home building process, as with traditional construction, is to create a blueprint. The house blueprint is created using a 3D modeling software programme and can be easily customized to meet the needs of the homeowner.
2. Send the design to the printer.
Feed the design to the 3D printer once the blueprint is approved. This is known as the preparation stage of the process. Once the digital file has been processed by the printer, it is time to prepare the build platform and fill the raw materials in order to get the project ready for execution.
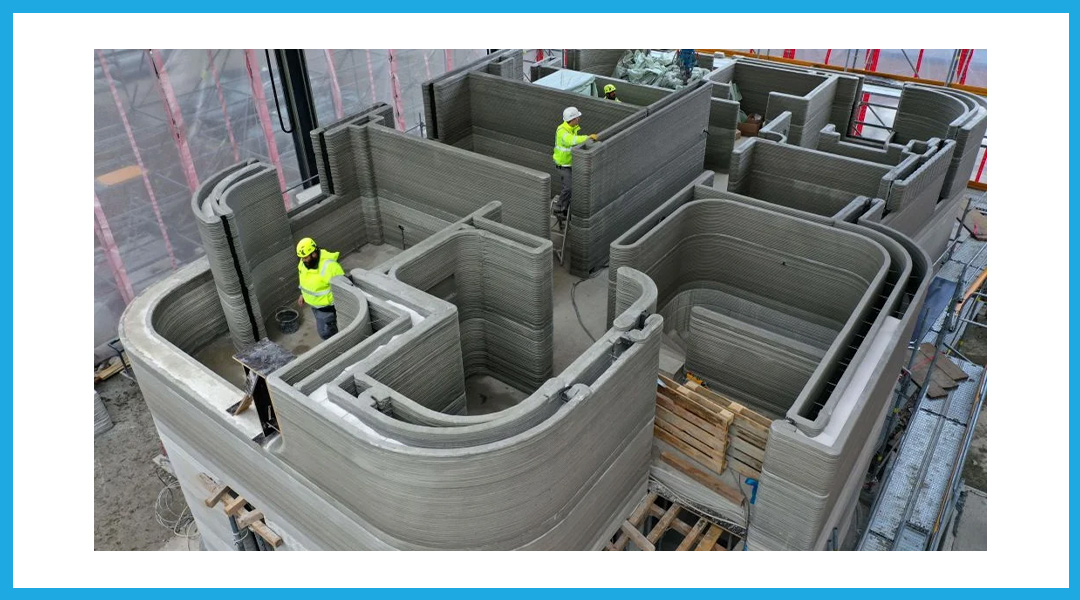
3. Robotic arm prints layer by layer.
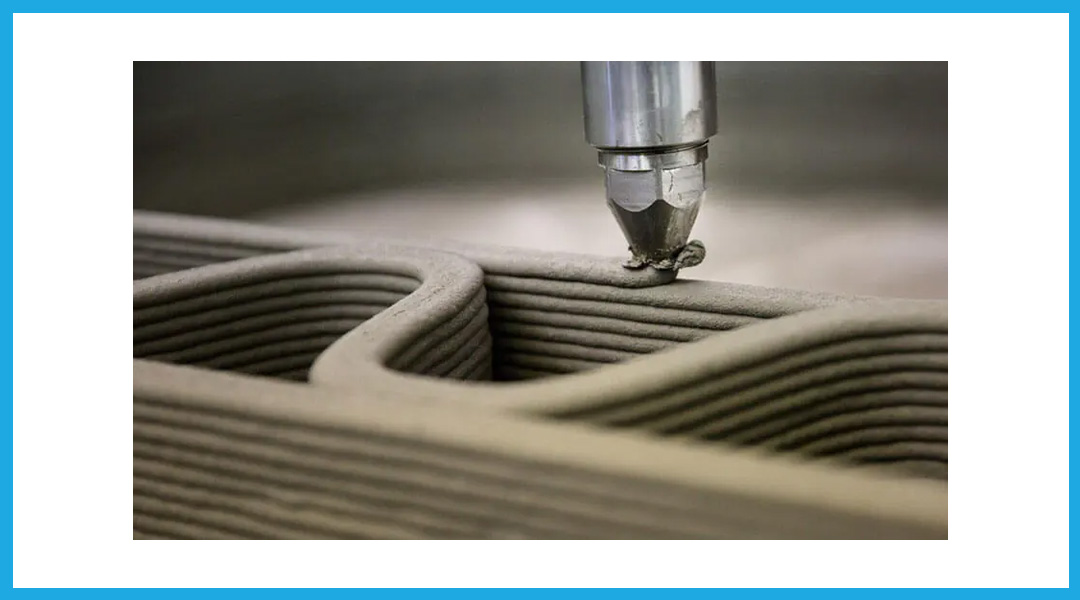
The robotic arm moves along the rail from place to place, laying the paste-like concrete mixture. Optimized cement-based mortar material is used in 3D printing printers. You simply press the “print” button, and the printer begins building, just like a normal printer.
The mortar used in 3D printed construction is often a proprietary material that ensures proper mixing ratios for laying paste on top of each other perfectly, without developing shrinkage or cracks.
3D printers print materials layer by layer using additive manufacturing. Material extrusion is the process of heating the printing material and then forcing it out through the nozzle. A concrete dryer allows the building material to solidify quickly before adding another layer.
4. Install windows, doors, plumbing, and electrical requirements.
When the home’s structure has been completed and the rails have been removed from the job site, it is time to add additional home features. Workers come to the construction site to finish the project by installing other items such as windows, doors, and so on, as well as plumbing and electrical wiring.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing in Construction
The main advantages of 3D home construction are:
Reduction in construction time
Using a 3D printer to complete a building project can drastically reduce construction time. A house built with 3D technology can be completed in a matter of days, as opposed to months for a traditional built structure. This can be extremely useful in an emergency situation where structures must be built as quickly as possible.
Reduction in construction costs
Because of reductions in raw materials and, more importantly, labor, 3D-printed buildings have much lower construction costs than traditional methods. The use of 3D printers for the majority of construction on an architectural project can reduce labor costs by up to 80%. Production costs are also reduced by eliminating the need for excess inventory, reducing waste, and taking other steps.
Versatility
Homebuyers can use 3D technology to customize their home shape. There can be a large variety of building designs.
Sustainability
As 3D printed constructions involve a much shorter supply chain and less waste, these homes are more environmentally friendly.
The major disadvantages of 3D printed home construction are:
Raw Materials are not easily available
The raw materials used in 3D-printed houses are different from that used in traditional construction. There are also very few materials available today that can be used in a 3D printer. Furthermore, the majority of printers require specific materials. This means that the raw material from one printer may not be usable in another.
Reduces job opportunities
In this age of digitalization, many jobs have already been automated. Once fully developed, 3D printing technology will undoubtedly have an impact on labor and the housing industry. The demand for skilled construction workers will fall, putting them in jeopardy. It will also endanger the livelihoods of those who provide construction equipment and materials.
Difficult to correct an error
The 3D printer prints out the entire model or design in one go. If there is a fault in the design, the printer can’t be stopped in between.
These are some Q&As about 3D printing construction that you can also check out.
How concrete is used in 3D printing construction
Buildability and extrudability are vital design properties for the mix used in 3D printed construction. Extrudability refers to the ability of the mixture to pass through nozzles in the printing head, whereas buildability refers to the ability to support additional layers. These properties are determined by the mix of design and materials used.
Due to its low cost and wide availability, Portland cement is the most frequently used component in the concrete mix for both traditional and 3D-printed construction. For 3D printed applications, however, its lengthy setting time and weak bonding power are disadvantages.
Polymers and other admixtures are frequently added to improve the properties of the mix, such as decreasing shrinkage and increasing adhesion. Some of these polymers, which also have the added advantages of crack repair and resistance, include rubber, mixed sand aggregates, carbon-sulfur polymers, and geopolymers.
Companies that offer 3D printing homes (or are working on the technology) have developed their own special concrete mixtures and are introducing them to their equipment with closed-use compatibility.
How Aggregates are used in 3D Printed Construction
Aggregates are a component of the concrete mix that act as reinforcement, increasing the overall strength of the composite material. When it comes to concrete mix design, aggregate content, and selection are just as important as the cementitious materials used.
Particle size, in particular, has a significant impact on 3D-printed concrete mixes. Particle sizes that are too large may clog the 3D printer’s nozzle, whereas aggregates that are too small reduce the strength of the mix and may cause cracking. To ensure smooth extrusion, the maximum aggregate particle size for the mix should be less than 1/10 of the nozzle diameter.
Natural aggregates like sand and gravel are preferred because they require less energy to produce.
What are some current applications of 3D printing in construction?
Current applications of 3D printing in construction include the printing of walls, floors, and other structural components, as well as the creation of molds for concrete casting. There are also some experimental applications in the construction of bridges and other large-scale infrastructure.
What is the future of 3D printing in construction?
The future of 3D printing in construction is expected to involve the use of more advanced materials and printing techniques, as well as the integration of 3D printing with other construction technologies such as robotics and artificial intelligence. It may also lead to new methods of construction, such as on-site printing, and the creation of entirely new types of structures.